Overview
You can run exports on demand, or set up daily, weekly and monthly schedules. Each export lets you pick the datasource, the file type to save the data as, and where the export should be sent or saved.
Recurring schedules export any records that have been updated since the schedule last ran. One-off exports let you pick the start and end date for the export range.
Current Schedules
The first page of the exporter lists existing schedules and lets you create a new export.
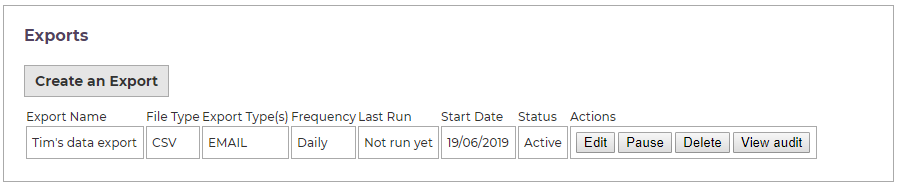
This list only includes active schedules. If an export was run as a one-off, or if the final date of a schedule has passed, the export won't be listed.
User Permissions
The data exporter uses a workflow process. Your iCM user needs to be aliased to a website user that is in the DATAEXPORTER user group to be able to create schedules
Editing Schedules
Editing a schedule reloads the same form used to create them, pre-populated with the current values. All fields can be changed and the schedule re-saved.
Pausing Schedules
Pausing an export schedule removes it from the list of exports to run. Resuming a paused schedule adds it back to the list and it will run the next time its scheduled repeat is reached.
Deleting Schedules
Deleting a schedule removes it from the list and terminates its associated process instance.
Audits
The audit button displays information about the previous 50 runs of the export schedule.
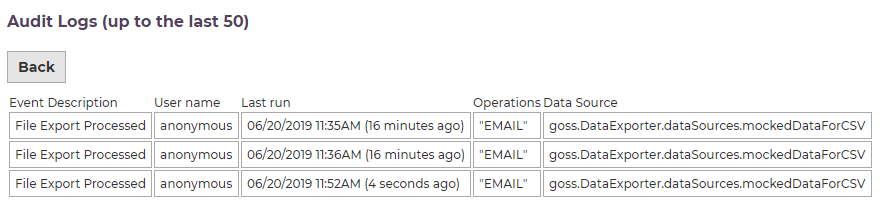
Note that because a schedule removes itself from the list when its end date is reached, it is not currently possible to view the audit information for schedules that are no longer running.
Creating and Editing an Export
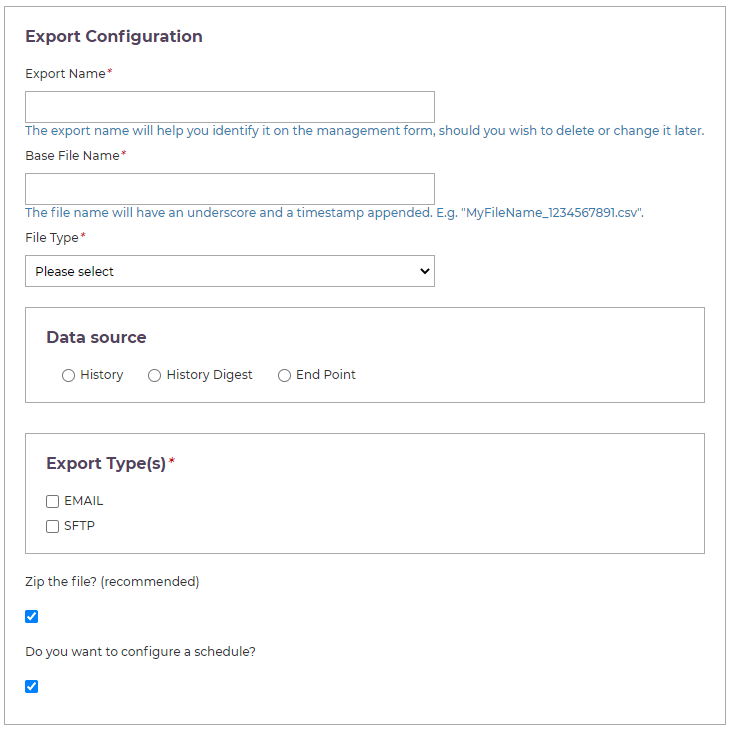
Name
Set a name for the scheduled export and a name for the file (which will be automatically appended with the timestamp of the export).
File Type
The File Type drop-down lists all of the available file types you can export the data as. Each type exists as a "file generator" end point in the Data Exporter's goss.DataExporter.fileGenerators namespace. The standard types are CSV and JSON.
Data Source
The data you export is found in the platform's History service. You can choose whether you want to export directly from history, export from digested histories (see History Digests for more information), or use custom end points to perform the export.
History
The history exporter exports histories that have been updated within a certain time period. Pick "History" as the data source to see a drop-down list of every history "labela" value. Pick the type of history you would like to export.
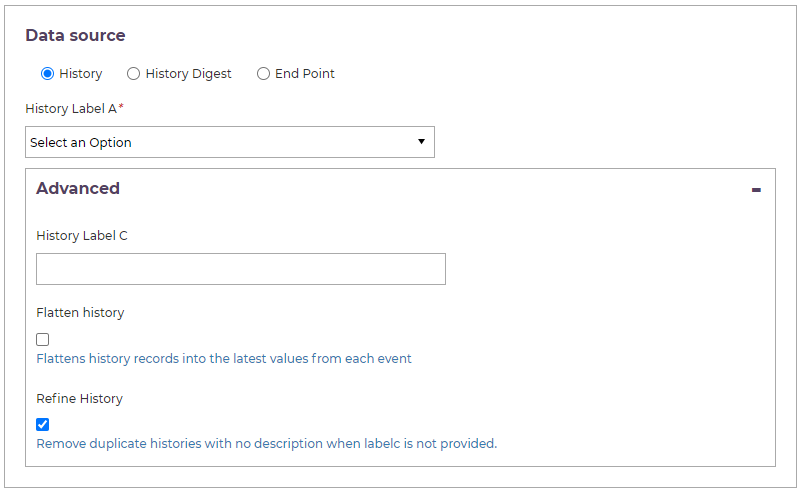
If you don't enter a labelc value (in the advanced section below), the exporter will assume a labelc: null. It's not possible to export all labelc type histories for a given labela record.
When you are setting up a schedule for the export, the start date of the schedule, set on the next page of the scheduler, determines the age of the histories that will be exported. The export range is calculated from when the schedule runs, back to your chosen start date. A repeating schedule of history exports will only export histories that have been updated since the schedule last ran.
For example, if your schedule runs daily, each export will include any histories that have been updated in the past day.
Volumes of Data
The exporter is designed to run regularly, perhaps on a daily or weekly basis, exporting new data written since the last export. Exporting large volumes of data will have an impact on performance.
Advanced
Enter the labelc value of the specific histories you would like to export.
The "flatten" history option will combine the events in the history into one record, displaying the most recent value for any fields with the same name that repeat across events.
The "refine history" option can be used to exclude any history events that don't have a historyDescription (see Conventions - Standardising History Data).
History Digest
Pick a history digest from the list to export all of the digested history data.
End Point
All of the end points in the goss.DataExporter.dataSources namespace are listed here. You'll find any product specific end points we have written listed here.
Export Types
Choose whether the export should be emailed or uploaded somewhere via SFTP. These options are configured later in the form.
Take care using email. You should not email anything that contains personal data. Email attachments are also subject to file size limits (around 30MB)
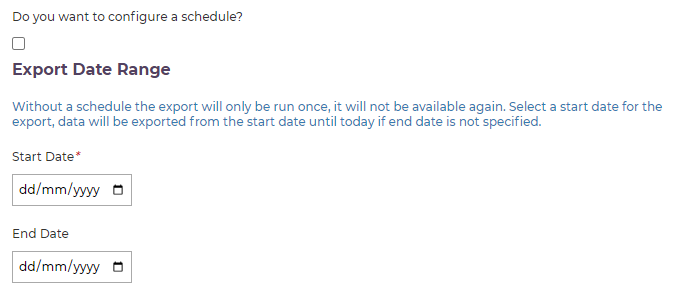
Create a Schedule or Pick a Date Range
Tick this box to set up a schedule later in the form (see the Scheduling page later).
Clear the box if you are creating a one-off export to run now. This lets you enter a start and end date to define the range of your export:
Email and SFTP Configuration
Email Configuration
Use the Email, Name and Add buttons to build up a table of addresses the export file should be sent to. If you'd like to customise the email body text, and you have the Comms Manager installed, check the box to reveal inputs for the application, template and language you'd like to use.
Note that emails will only be sent when there is data to export. If there's no new data the email isn't sent.
SFTP Configuration
If you selected SFTP as an export type, pick your SFTP configuration from the drop-down.
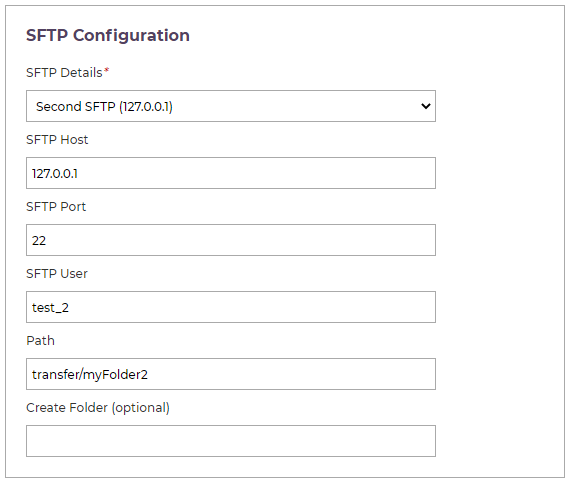
All of the other fields are read-only. Your SFTP details are set in the exporter's configuration end point, see Data Exporter Configuration.
Testing the Export
Checking this box will perform the export as soon as you navigate to the next page of the configuration form.
Scheduling
This section of the form lets you set up the export to happen on a future date, or to repeat at daily, weekly, monthly or annual intervals.
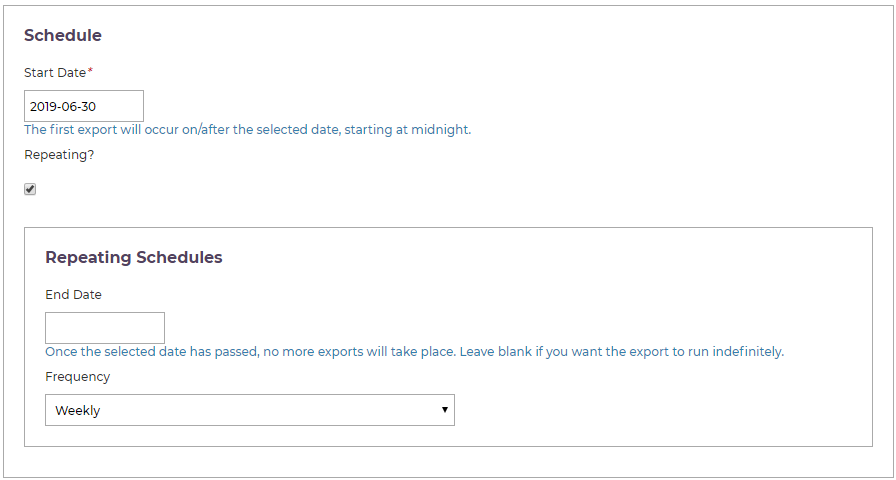
The start date you enter determines the age of the histories that will be exported. For example, if you want to export histories updated since January 2023, set the start of your schedule back to that date.
When you create a repeating export, each repeat of the scheduler exports new data that has been updated since the export last ran.
When a schedule reaches its end date, it removes itself from the scheduled list.
Volumes of Data
The exporter is designed to run regularly, perhaps on a daily or weekly basis, exporting new data written since the last export. Exporting large volumes of data will have an impact on performance.
The exporter exports histories that have been updated in the set time period. That means the same history record will appear in multiple exports if it is updated within each reporting period.




